Web Technology
The Pros and Cons of Cloud Computing You Need To Know
Cloud computing has transformed how businesses manage technology. By offering cloud-based services on demand, companies can scale quickly, cut infrastructure costs, and enhance collaboration. This guide explores the pros and cons of cloud computing services to maximize their potential for your business success and avoid any potential pitfalls.

What Is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing refers to delivering computing services—like storage, databases, networking, and software—over the Internet via remote servers hosted by cloud providers. It eliminates the need for physical infrastructure, enabling businesses to access resources flexibly and efficiently.
Key Features of Cloud Computing
- On-Demand Services: Access resources anytime, anywhere.
- Scalability: Adjust computing power or storage needs instantly.
- Pay-As-You-Go Pricing: Only pay for what you use, reducing operational costs.
- Global Reach: Deploy applications worldwide with minimal latency.
Role in Modern Application Development
Cloud computing drives cloud-native development, enabling scalable and resilient applications.
Unlike traditional monolithic architectures, cloud-native applications use microservices and containerization, offering:
- Microservices Architecture: Breaks apps into smaller, independently deployable services.
- Containers: Tools like Docker and Kubernetes streamline scalability and reliability.
Hybrid Cloud Solutions
Businesses often adopt a hybrid cloud model to balance the benefits of public cloud scalability with private cloud security. This approach is ideal for companies needing flexibility and compliance.
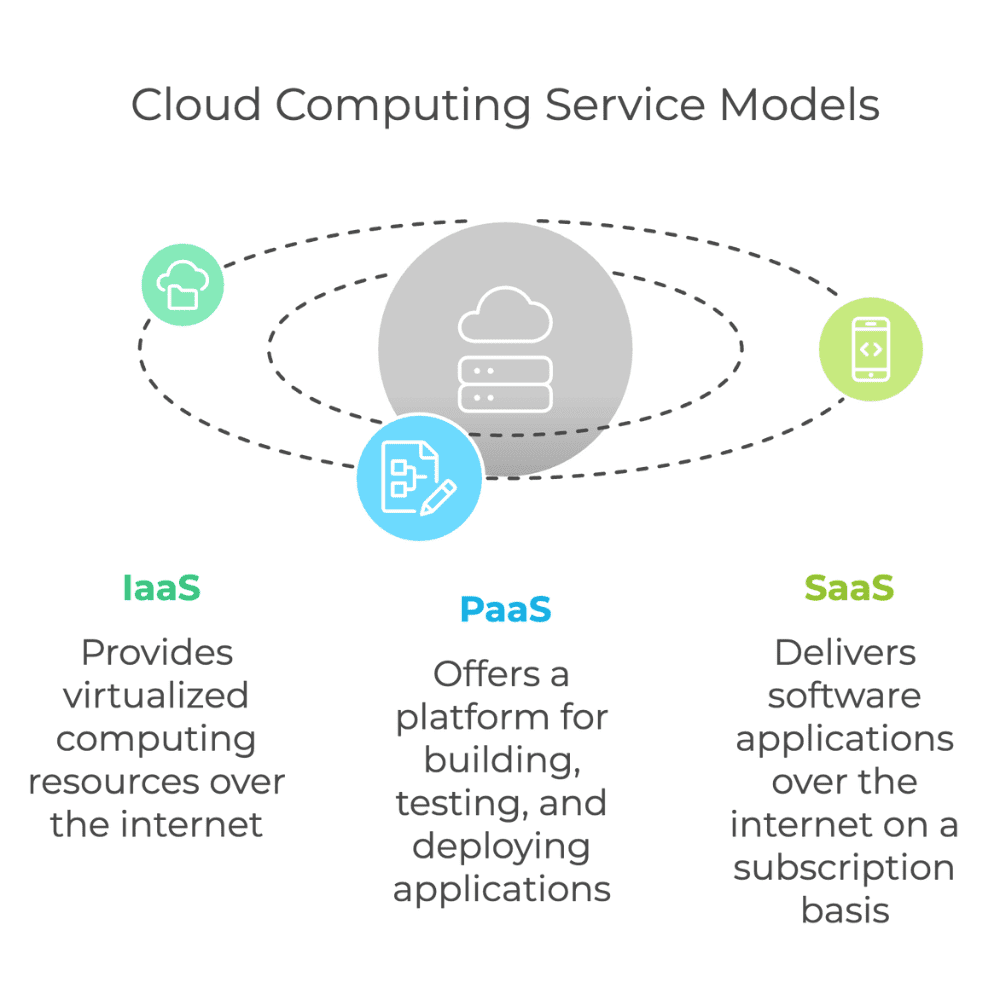
What Are Common Cloud Computing Service Models?
Cloud computing offers various service models, each catering to specific business needs. Key examples include:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Provides virtualized computing resources over the internet, including storage and networks. Learn more about IaaS.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Offers a platform for building, testing, and deploying applications. Ideal for developers looking to focus on app creation without managing the underlying infrastructure.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Delivers software applications over the internet, typically on a subscription basis, like Google Workspace or Microsoft 365.
|
Service Type |
Description |
Examples |
|
IaaS |
Provides computing infrastructure, including storage and networking |
Amazon EC2, Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines |
|
PaaS |
A platform for developing and managing applications |
Google App Engine, Heroku |
|
SaaS |
Software applications available online |
Salesforce, Google Workspace |
Public Cloud vs. Private Cloud
- Public Cloud: Shared infrastructure for cost efficiency and scalability.
- Private Cloud: Dedicated resources for enhanced control and security, ideal for industries with strict compliance needs.
Quick Breakdown of the Advantages and Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing services offer a dynamic way to access IT resources, providing unparalleled scalability, cost savings, and flexibility.
However, they also come with challenges like security risks, vendor lock-in, and dependence on network reliability. Understanding these trade-offs can help businesses maximize benefits while mitigating potential drawbacks.
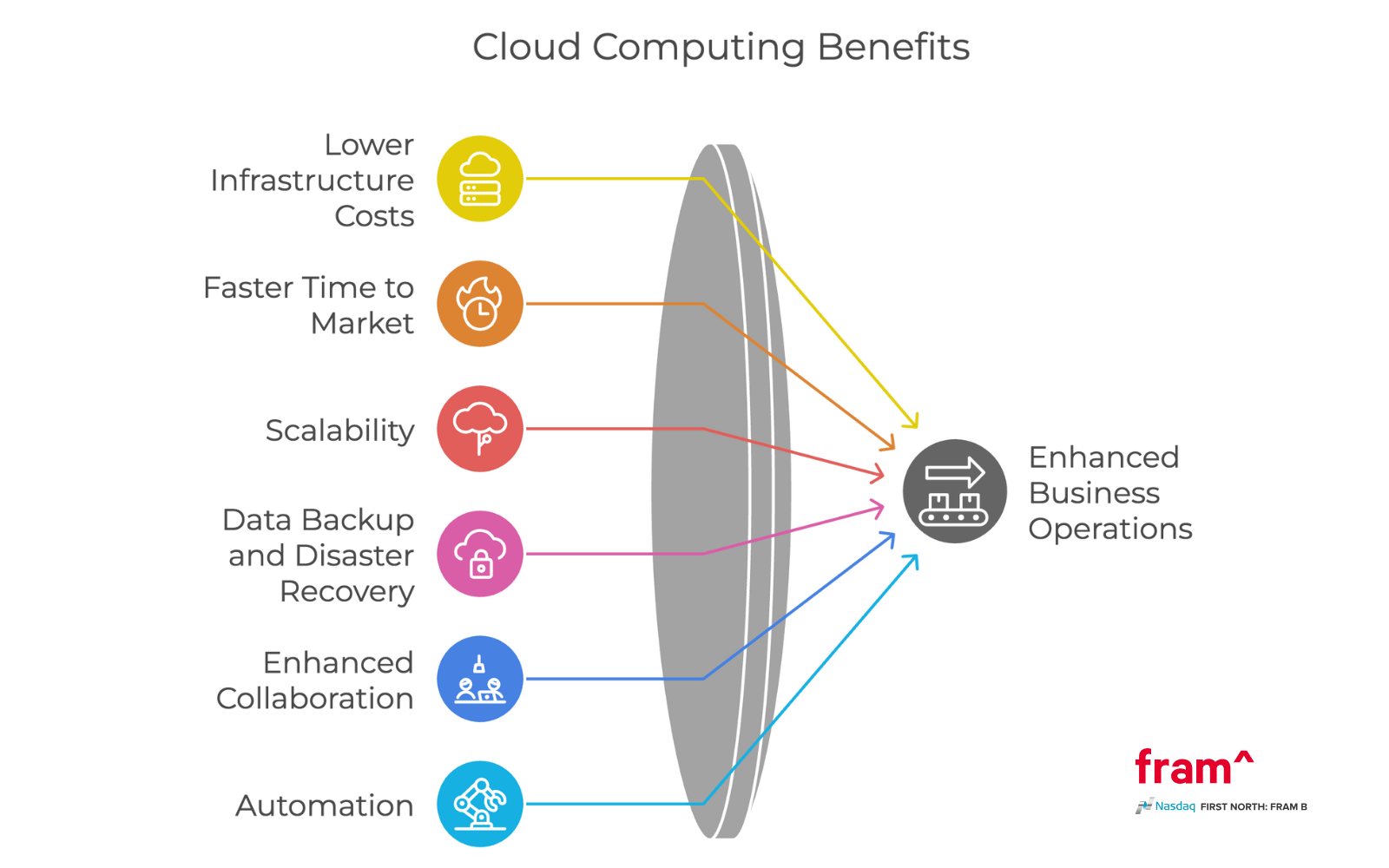
Cloud Computing Pros
- Cost Savings: Eliminates upfront infrastructure expenses, saving on hardware and maintenance.
- Faster Time to Market: Quick deployment accelerates product launches.
- Scalability: Seamlessly scale resources up or down to meet demand.
- Collaborative Benefits: Teams collaborate in real-time using cloud-based services.
- Data Backup and Disaster Recovery: Minimize downtime during natural disasters or hardware failures.
- Automation: Automate repetitive tasks to boost efficiency.
Cloud Computing Cons
- Vendor Lock-In: Migration between cloud service providers can be challenging.
- Internet Dependency: Requires reliable internet connection, so disruptions can affect operations.
- Security Risks: Public cloud systems require robust encryption and access controls.
- Hidden Costs: Mismanaged cloud resources or storage space can inflate expenses (be sure to check out our digital managed services).
- Service Interruptions: Downtime due to technical issues or provider maintenance can disrupt business continuity.
Key Technical Benefits of Cloud Computing
1. Lower Infrastructure Costs
One of the most compelling benefits of cloud computing is cost reduction. Businesses can eliminate upfront hardware expenses, such as purchasing servers, storage devices, and networking equipment.
Cloud providers like Google Cloud and Alibaba Cloud manage infrastructure setup, maintenance, and updates, allowing companies to focus on innovation and growth rather than IT logistics.
In addition, cost savings extend to operational expenses, as businesses no longer need to hire specialized staff to maintain on-premises servers. Flexible pricing models, like pay-as-you-go, further ensure that companies only pay for the resources they use.
And we here at fram – a software development company in Vietnam, have been helping our partners with this since 2013!
2. Faster Time to Market
Cloud computing enables rapid deployment of applications and services, reducing the time needed for development and rollout. Platforms like AWS and Microsoft Azure provide pre-configured tools and templates for development, testing, and deployment, significantly shortening project timelines. Learn more in our full breakdown of Azure vs AWS.
This agility gives businesses a competitive edge, allowing them to respond to market demands, launch products faster, and iterate based on user feedback without delays caused by infrastructure constraints.
3. Scalability
Scalability is at the core of cloud computing’s appeal. Whether your business experiences seasonal spikes or sudden traffic surges, cloud platforms allow seamless scaling up or down of resources in real time.
For example, e-commerce platforms can increase server capacity during holiday sales, while startups can scale as their user base grows. This resource flexibility ensures you pay for your needs without overprovisioning or underutilizing infrastructure.
4. Data Backup and Disaster Recovery
Cloud computing simplifies disaster recovery and data backup processes, ensuring business continuity during unforeseen events like natural disasters or hardware failures. Cloud providers offer automated backup systems that store data in geographically distributed locations, reducing the risk of data loss.
In the event of an outage, businesses can quickly restore operations using backup data from remote servers. This minimizes downtime and mitigates the financial impact of disruptions.
5. Enhanced Collaboration
Cloud-based tools enable teams to collaborate in real time, regardless of location. Employees can access shared files, communicate through integrated platforms, and work on projects simultaneously, improving productivity and reducing bottlenecks.
For example, cloud-based storage solutions like Google Drive or Microsoft OneDrive allow team members to edit documents together, ensuring seamless communication across geographies and time zones.
6. Automation
Cloud platforms offer built-in automation tools that streamline repetitive tasks, such as resource provisioning, data processing, and system monitoring. Automation reduces manual errors, enhances efficiency, and allows IT teams to focus on strategic initiatives.
For example, AWS’s automation features include scheduled backups, auto-scaling, and serverless computing with Lambda functions, empowering businesses to operate with minimal manual intervention.
Limitations and Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
Despite the significant advantages, there are some limitations you’ll want to be aware of.
1. Vendor Lock-In (Migration Challenges)
While cloud computing offers flexibility, migrating data and applications between providers can be costly and technically challenging.
Proprietary tools, data formats, and workflows often tie businesses to a specific cloud services provider, making switching providers or adopting multi-cloud strategies difficult.
This vendor lock-in can limit agility and make businesses dependent on a single provider’s pricing, service quality, and feature set.
2. Network and Provider Dependence
Cloud computing relies heavily on stable internet connectivity to access resources hosted on remote servers. Outages or slow connections can result in downtime, directly impacting business operations.
Additionally, businesses are dependent on the reliability and performance of the cloud provider’s infrastructure. Public cloud providers may experience disruptions during peak usage or scheduled maintenance, which could delay critical processes.
3. Service Interruptions (Reliability)
Despite their reliability, even top-tier providers like AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure can face service interruptions due to hardware failures, software bugs, or cyberattacks.
Without a disaster recovery plan, businesses may face significant downtime, disrupting their ability to meet customer demands.
Planning for redundancy and utilizing hybrid cloud models can help mitigate these risks by balancing workloads across public and private environments.
4. Security Risks
Data stored on public cloud systems can be vulnerable to breaches, requiring robust security measures such as encryption, access controls, and regular audits.
Different deployment models address security concerns:
- Public Cloud: Shared infrastructure may expose data to potential threats.
- Private Cloud: Offers enhanced security, suitable for industries with strict compliance standards.
- Hybrid Cloud: Combines public and private environments to provide flexibility while safeguarding sensitive information.
5. Storage Space and Resource Management
While cloud storage is highly scalable, excessive data accumulation without proper management can lead to inflated costs. Businesses must regularly evaluate and optimize their storage space usage to avoid paying for underutilized resources.
For example, a lack of data lifecycle policies can result in businesses retaining outdated data indefinitely, driving up operational costs. Implementing regular audits and resource monitoring tools can help manage these challenges effectively.
Why the Pros Outweigh the Cons
Despite its limitations, cloud computing remains a transformative technology for businesses. The ability to reduce costs, improve agility, and enhance collaboration far outweighs concerns like vendor lock-in or internet dependence.
By adopting best practices such as regular audits, redundancy planning, and investing in cloud security, businesses can maximize the benefits while mitigating potential risks.
With cloud computing, businesses unlock the potential for growth, scalability, and innovation that traditional infrastructure simply cannot match.
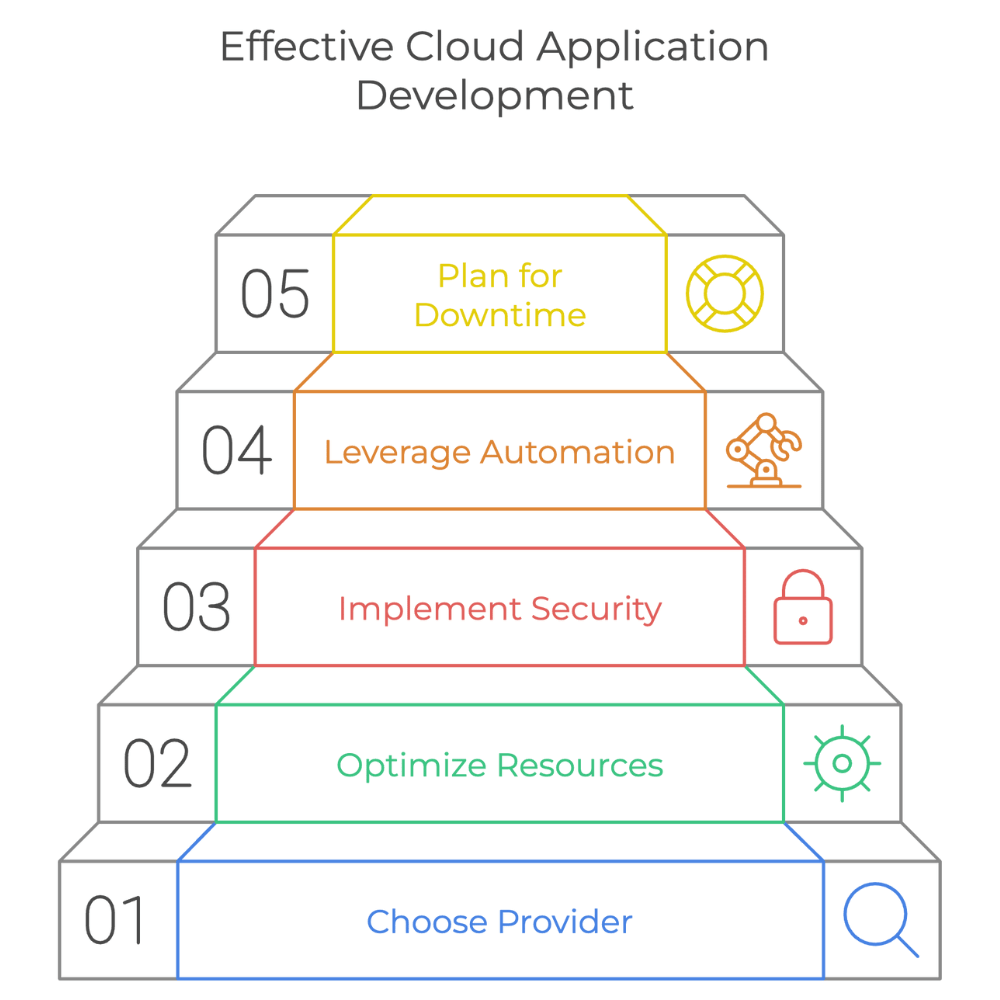
Best Practices for Cloud Application Development
To make the most of cloud computing, follow these best practices:
- Choose the Right Provider: Evaluate providers based on cost efficiency, scalability, and security features.
- Optimize Resource Usage: Regularly review storage space and performance metrics to avoid unnecessary expenses.
- Implement Security Measures: Secure data with encryption and access controls.
- Leverage Automation: Use tools to automate repetitive tasks, improving operational efficiency.
- Plan for Downtime: Prepare for potential interruptions with redundancy and business continuity plans.
At Fram: Harnessing Cloud Computing for Scalable Solutions
At Fram, we use private and public cloud solutions to develop scalable applications for businesses of all sizes. From startup monolithic apps to enterprise-level microservices serving millions of active users, our expertise ensures efficient deployment and seamless management.
Our team leverages tools like AWS CDK, CloudFormation, and Cloud Watch to automate infrastructure management, enabling cost savings and improved operational efficiency. Cloud-based services enhance collaboration across teams, ensuring smooth project execution.
FAQ on Cloud Computing Pros & Cons
Which Providers Dominate the Cloud Market?
The top cloud providers are Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). Each offers extensive services with unique strengths. Learn more about AWS, Azure, and GCP.
How Can I Migrate to the Cloud?
Cloud migration requires careful planning, including assessing data sensitivity, determining optimal service models, and choosing the right provider. Start with a migration plan, assess your needs, and choose the right cloud services provider. Engaging a trusted partner like Fram simplifies the process.
How Does Pricing for Cloud Services Work?
Most cloud providers offer pay-as-you-go pricing, meaning you pay only for the resources you use, and scalability to reduce upfront and operational expenses, offering significant cost efficiency. Additional savings are possible through long-term commitments or reserved instances.
How to Choose the Best Cloud Development Partner?
Cloud computing offers transformative benefits, from cost savings and scalability to improved collaboration and automation. However, it’s essential to be aware of the potential limitations, such as vendor lock-in and security risks. By understanding both the pros and cons, businesses can make informed decisions and unlock the full potential of cloud technology.
If you’re ready to harness the power of the cloud, consider partnering with a team that understands both the opportunities and challenges of cloud development. With the right guidance, cloud computing can be a valuable asset to drive growth and efficiency.
Pros and Cons of Cloud Computing in Closing
Cloud computing empowers businesses with cost savings, scalability, and improved collaboration. While it has limitations like vendor lock-in and security challenges, the benefits far outweigh the drawbacks for most organizations.
Partner with Fram to unlock the potential of cloud technology. With our expertise, we’ll help you build scalable, efficient systems tailored to your needs. Contact us below for a free consultation!